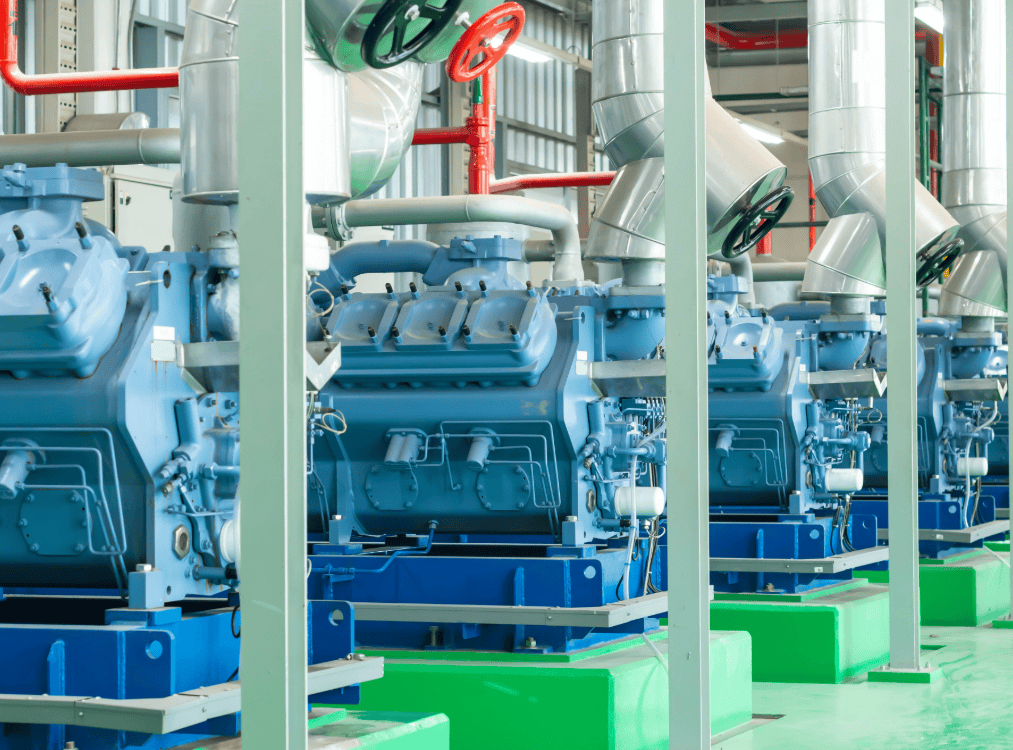
Key Requirements for Refrigerant Gas Detection in Chiller Rooms
In the realm of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), ensuring the safety and efficiency of chiller rooms is paramount. One critical aspect of maintaining a safe environment in these facilities is effective refrigerant gas detection. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provides essential standards and guidelines that govern refrigerant gas detection systems. This blog delves into the key ASHRAE codes relevant to refrigerant gas detection in chiller rooms, including installation and maintenance requirements.
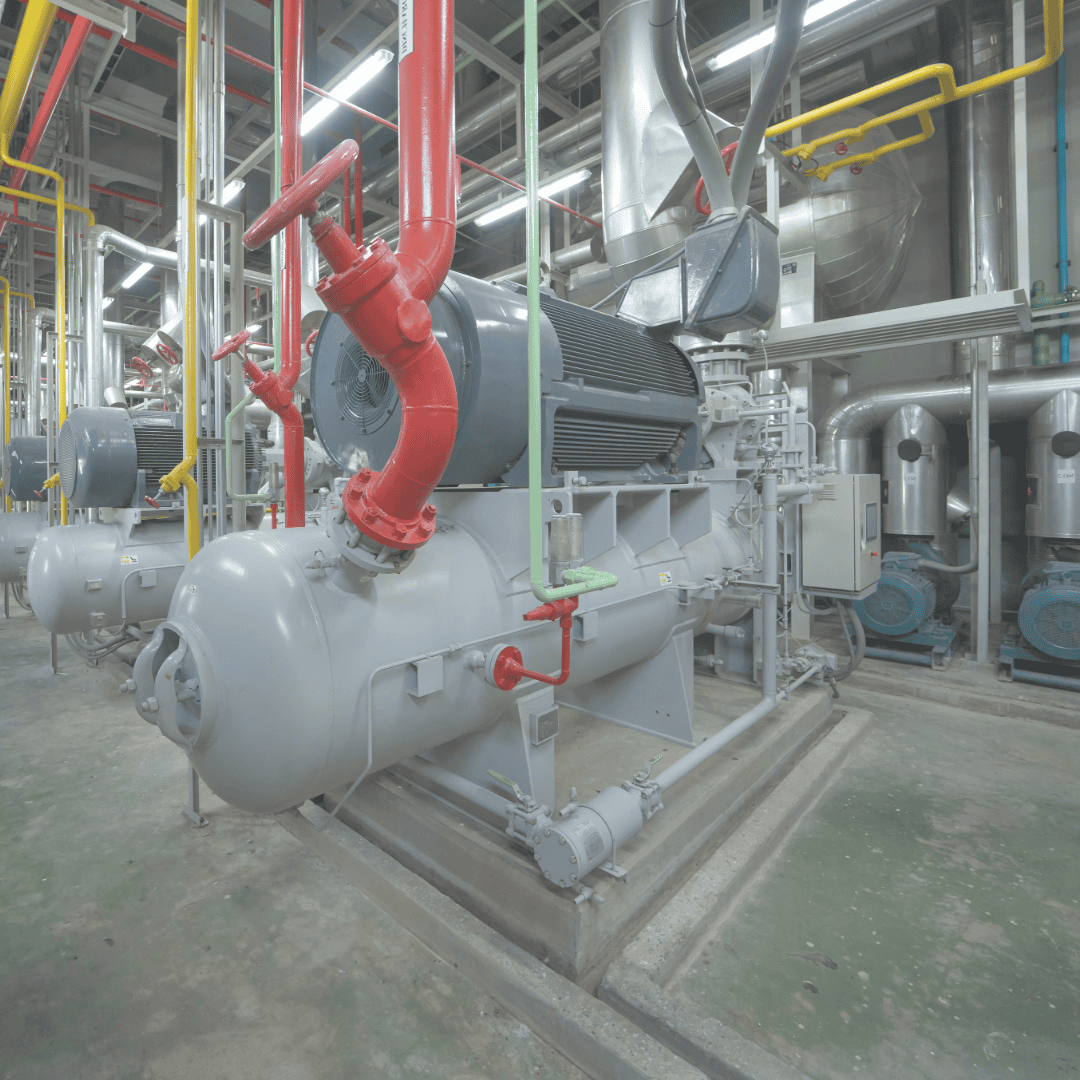
The Importance of Refrigerant Gas Detection
Refrigerant gases play a pivotal role in the operation of chillers and HVAC systems. However, they can also pose significant risks, including environmental damage, health hazards, and fire risks if not properly monitored. Effective refrigerant gas detection systems help mitigate these risks by identifying leaks early and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Relevant ASHRAE Standards
1. ASHRAE Standard 15: Safety Standard for Refrigeration Systems
ASHRAE Standard 15 outlines essential safety protocols for refrigeration systems. Key requirements include:
- Detection of Refrigerant Leaks:
“Refrigerant detection systems shall be installed in areas where refrigerants could leak and where their concentration may pose a hazard.”
This standard mandates that refrigerant gas detection systems be installed in areas such as chiller rooms, compressor rooms, and any area with refrigerant piping. - Alarm Systems:
“Where the refrigerant concentration exceeds the allowable limits, audible and visible alarms shall be provided.”
This requirement ensures that detection systems are equipped with both audible and visual alarms to alert personnel in the event of a leak, promoting quick action. - Installation and Maintenance:
“Gas detection systems shall be installed and maintained in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.”
Regular maintenance checks are crucial to ensure systems operate effectively and comply with safety standards.
2. ASHRAE Standard 62.1: Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality
While primarily focused on ventilation, ASHRAE Standard 62.1 also addresses the importance of controlling refrigerants to ensure adequate indoor air quality. Key points include:
- Ventilation Requirements:
“Ventilation shall be provided to dilute and remove contaminants, including refrigerant gases.”
Proper ventilation can help dilute the concentration of refrigerant gases, reducing the risk of exposure to harmful levels. - Monitoring Indoor Air Quality (IAQ):
“Monitoring systems shall be in place to assess the quality of the air in occupied spaces.”
Implementing gas detection systems helps monitor IAQ, ensuring that refrigerant leaks do not compromise the health and safety of building occupants.
3. ASHRAE Standard 34: Designation and Classification of Refrigerants
ASHRAE Standard 34 classifies refrigerants based on their safety and environmental impact. Key considerations include:
- Toxicity Levels:
“Refrigerants shall be classified according to their toxicity, flammability, and environmental effects.”
This classification helps engineers determine which refrigerants require more stringent monitoring and detection protocols. - Flammability:
“Refrigerants classified as flammable shall be subjected to additional safety precautions.”
Understanding the flammability of various refrigerants is crucial for determining appropriate gas detection measures in chiller rooms.
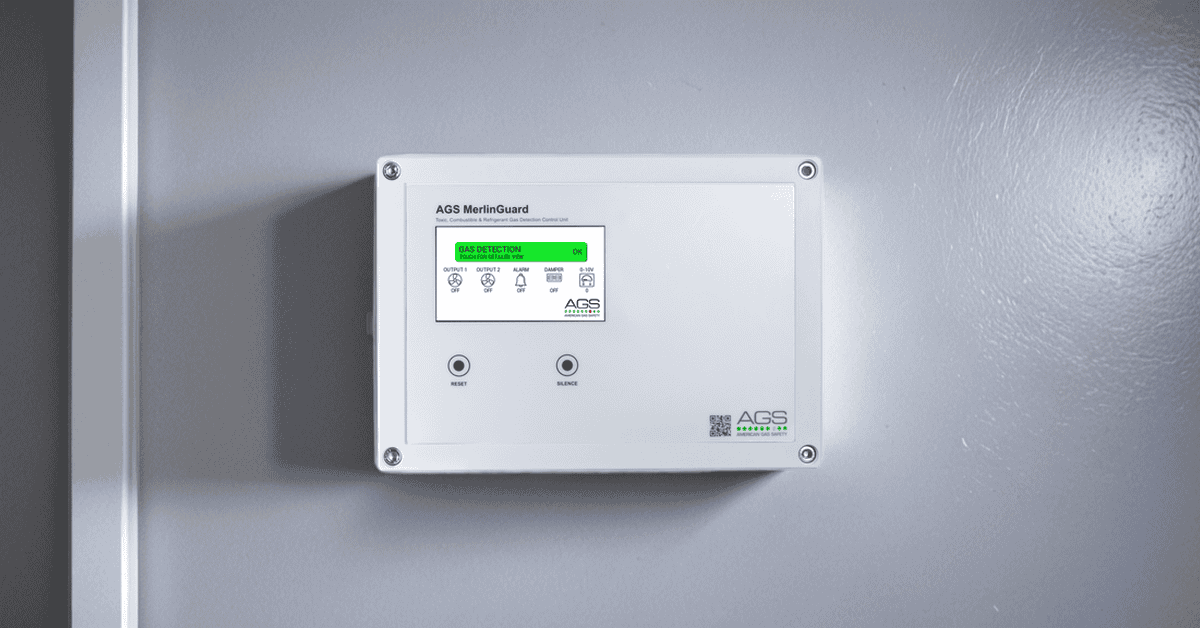
Installation Guidelines
Installing a refrigerant gas detection system, such as the MerlinGuard by American Gas Safety, in compliance with ASHRAE codes involves several critical steps:
- Location of Detectors:
Position detectors in areas where refrigerant leaks are most likely to occur, such as near compressor units, in enclosed spaces, and along refrigerant piping. - Type of Detectors:
Select appropriate detectors for the specific refrigerants used in the system. Some detectors are designed for specific gases, such as R-22 or R-410A. - Alarm Configuration:
Ensure that the alarm settings are configured to respond appropriately to different concentrations of refrigerants, based on ASHRAE guidelines. - Regular Maintenance:
Implement a routine maintenance schedule to test and calibrate detectors, ensuring they are functioning correctly and within ASHRAE standards.
Maintenance Considerations
Maintenance is a critical aspect of ensuring the ongoing effectiveness of refrigerant gas detection systems:
- Routine Testing:
Regularly test alarm systems to verify that they activate at the correct thresholds. - Calibration:
Follow manufacturer guidelines for calibration to ensure accuracy in detecting refrigerant gases. - Documentation:
Maintain detailed records of maintenance activities, including tests performed, results, and any corrective actions taken.
Understanding and complying with ASHRAE codes is essential for the effective installation and maintenance of refrigerant gas detection systems in chiller rooms. By adhering to these standards, facility managers and mechanical engineers can create safer environments, protect personnel, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Proper gas detection not only safeguards health and safety but also enhances the efficiency and reliability of HVAC systems.
For more information on refrigerant gas detection solutions, consider exploring products offered by American Gas Safety, which are designed to meet the highest standards of safety and efficiency in chiller room applications.